Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- vim 자동정렬
- x-window
- linux log
- 데이터베이스 갱신
- 리눅스
- db 백업
- alter 문법
- 리눅스 gui
- vim 정렬
- db덤프
- mysql 계정생성
- alter 명령어
- 컴파일 설치
- 리눅스 로그
- 컴파일러 입문
- mysql update
- mysql 갱신
- 렉스 컴파일
- 로그 삭제
- db 덤프
- 자동정렬
- lex 컴파일
- mysql alter
- mysql 권한부여
- mysql 계정삭제
- 데이터 갱신
- 리눅스 로그 삭제
- 렉스
- x윈도우
- lex compiler
Archives
- Today
- Total
It's under your control.
OCP license.E05.130628 본문
ALTER TABLE Statement
Use the ALTER TABLE statement to add, modify, or drop columns:
Flashback Version Query
CUBE Operator
• CUBE is an extension to the GROUP BY clause.
• You can use the CUBE operator to produce crosstabulation values with a single SELECT statement.
.png)
Use the ALTER TABLE statement to add, modify, or drop columns:
| ALTER TABLE table ADD (column datatype [DEFAULT expr] [, column datatype]...); |
| ALTER TABLE table MODIFY (column datatype [DEFAULT expr] [, column datatype]...); |
| ALTER TABLE table DROP (column); |
SET UNUSED Option
• You use the SET UNUSED option to mark one or more columns as unused.
• You use the DROP UNUSED COLUMNS option to remove the columns that are marked as unused.
• You use the SET UNUSED option to mark one or more columns as unused.
• You use the DROP UNUSED COLUMNS option to remove the columns that are marked as unused.
| ALTER TABLE <table_name> SET UNUSED(<column_name>); OR ALTER TABLE <table_name> SET UNUSED COLUMN <column_name>; |
| ALTER TABLE <table_name> DROP UNUSED COLUMNS; |
Adding a Constraint Syntax
Use the ALTER TABLE statement to:
• Add or drop a constraint, but not modify its structure
• Enable or disable constraints
• Add a NOT NULL constraint by using the MODIFY clause
Use the ALTER TABLE statement to:
• Add or drop a constraint, but not modify its structure
• Enable or disable constraints
• Add a NOT NULL constraint by using the MODIFY clause
ON DELETE CASCADE : FK 가 참조하는 데이터가 지워지면, 자식테이블의 데이터도 같이 지워진다.
ON DELETE SET NULL : FK 가 참조하는 데이터가 지워지면, 자식테이블의 컬럼 데이터가 NULL로 변경된다.
Types of Multitable INSERT Statements
The different types of multitable INSERT statements are:
• Unconditional INSERT : 조건 없이 여러개의 table에 value를 넣을 때
The different types of multitable INSERT statements are:
• Unconditional INSERT : 조건 없이 여러개의 table에 value를 넣을 때
exmp) INSERT ALL
INTO sal_history VALUES(EMPID,HIREDATE,SAL)INTO mgr_history VALUES(EMPID,MGR,SAL)SELECT employee_id EMPID, hire_date HIREDATE,salary SAL, manager_id MGRFROM employeesWHERE employee_id > 200;
• Conditional ALL INSERT : 조건을 가지고 여러개의 table에 value를 넣을 때
exmp ) INSERT ALL
WHEN SAL > 10000 THENINTO sal_history VALUES(EMPID,HIREDATE,SAL)WHEN MGR > 200 THENINTO mgr_history VALUES(EMPID,MGR,SAL)SELECT employee_id EMPID,hire_date HIREDATE,salary SAL, manager_id MGRFROM employeesWHERE employee_id > 200;
• Conditional FIRST INSERT : FIRST는 ALL 과 달리 값을 대입하되, 위에서 값을 대입하면 삭제
exmp ) INSERT FIRST
WHEN SAL > 25000 THENINTO special_sal VALUES(DEPTID, SAL)WHEN HIREDATE like ('%00%') THENINTO hiredate_history_00 VALUES(DEPTID,HIREDATE)WHEN HIREDATE like ('%99%') THENINTO hiredate_history_99 VALUES(DEPTID, HIREDATE)ELSEINTO hiredate_history VALUES(DEPTID, HIREDATE)SELECT department_id DEPTID, SUM(salary) SAL,MAX(hire_date) HIREDATEFROM employeesGROUP BY department_id;
• Pivoting INSERT : 축을 변경하여
exmp ) INSERT ALL
INTO sales_info VALUES (employee_id,week_id,sales_MON)INTO sales_info VALUES (employee_id,week_id,sales_TUE)INTO sales_info VALUES (employee_id,week_id,sales_WED)INTO sales_info VALUES (employee_id,week_id,sales_THUR)INTO sales_info VALUES (employee_id,week_id, sales_FRI)SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID, week_id, sales_MON, sales_TUE,sales_WED, sales_THUR,sales_FRIFROM sales_source_data;
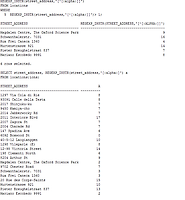
SQL> select * from SALES_SOURCE_DATA; EMPLOYEE_ID WEEK_ID SALES_MON SALES_TUE SALES_WED SALES_THUR SALES_FRI --------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- 176 6 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 SQL> SELECT * FROM sales_info; EMPLOYEE_ID WEEK SALES ----------- ---------- ---------- 176 6 2000 176 6 3000 176 6 4000 176 6 5000 176 6 6000 |
MERGE StatementMERGE Statement
• Provides the ability to conditionally update or insert data into a database table
• Performs an UPDATE if the row exists, and an INSERT if it is a new row:
– Avoids separate updates
– Increases performance and ease of use
– Is useful in data warehousing applications
• Provides the ability to conditionally update or insert data into a database table
• Performs an UPDATE if the row exists, and an INSERT if it is a new row:
– Avoids separate updates
– Increases performance and ease of use
– Is useful in data warehousing applications
* syntax
| MERGE INTO table_name table_alias USING (table|view|sub_query) alias ON (join condition) WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET col1 = col_val1, col2 = col2_val WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (column_list) VALUES (column_values); |
Flashback Version Query
| SQL> SELECT versions_starttime, versions_endtime, salary FROM employees VERSIONS BETWEEN scn minvalue and maxvalue where employee_id = 100; VERSIONS_STARTTIME VERSIONS_ENDTIME SALARY ----------------- ----------------- ---------- 28-JUN-13 12.33.49 PM 2000 28-JUN-13 12.33.43 PM 28-JUN-13 12.33.49 PM 1000 28-JUN-13 12.33.43 PM 24000 |
ROLLUP Operator
• ROLLUP is an extension to the GROUP BY clause.
• Use the ROLLUP operation to produce cumulative aggregates, such as subtotals
• ROLLUP is an extension to the GROUP BY clause.
• Use the ROLLUP operation to produce cumulative aggregates, such as subtotals
SQL> SELECT department_id, job_id, SUM(salary)
DEPARTMENT_ID JOB_ID SUM(SALARY) ------------- ---------- ----------- 10 AD_ASST 4400 20 MK_MAN 13000 20 MK_REP 6000 30 PU_CLERK 13900 30 PU_MAN 11000 40 HR_REP 6500 50 SH_CLERK 64300 50 ST_CLERK 55700 50 ST_MAN 36400 9 rows selected. SQL> SQL> SELECT department_id, job_id, SUM(salary)
DEPARTMENT_ID JOB_ID SUM(SALARY) ------------- ---------- ----------- 10 AD_ASST 4400 10 4400 20 MK_MAN 13000 20 MK_REP 6000 20 19000 30 PU_MAN 11000 30 PU_CLERK 13900 30 24900 40 HR_REP 6500 40 6500 50 ST_MAN 36400 50 SH_CLERK 64300 50 ST_CLERK 55700 50 156400 211200 15 rows selected. |
• CUBE is an extension to the GROUP BY clause.
• You can use the CUBE operator to produce crosstabulation values with a single SELECT statement.
.png)  |
.png)  |
GROUPING SETS
- 동일한 퀴리에 대해서 다양한 그룹핑을 정의 가능
- 개별로 그룹핑하여 UNION ALL한 경우와 동일하나, 성능적인 면에서 뛰어남
Scalar Subquery Expressions
• A scalar subquery expression is a subquery that returns exactly one column value from one row.
• Scalar subqueries can be used in:
– Condition and expression part of DECODE and CASE
– All clauses of SELECT except GROUP BY
• A scalar subquery expression is a subquery that returns exactly one column value from one row.
• Scalar subqueries can be used in:
– Condition and expression part of DECODE and CASE
– All clauses of SELECT except GROUP BY
.png)
WITH Clause : 별칭을 만들어서 재활용함으로써 좀더 효율적으로 쿼리를 관리함.
• Using the WITH clause, you can use the same query block in a SELECT statement when it occurs more than once within a complex query.
• The WITH clause retrieves the results of a query block and stores it in the user’s temporary tablespace.
• The WITH clause improves performance.
• Using the WITH clause, you can use the same query block in a SELECT statement when it occurs more than once within a complex query.
• The WITH clause retrieves the results of a query block and stores it in the user’s temporary tablespace.
• The WITH clause improves performance.
* Using the WITH clause, write a query to display the department name and total salaries for those departments whose total salary is greater than the average salary across departments.
WITH dept_costs AS (
avg_cost AS (
SELECT * FROM dept_costs WHERE dept_total >
ORDER BY department_name; |
'Works > OCP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| OCP license.E07.130702 (0) | 2013.07.06 |
|---|---|
| OCP license.E06.130701 (0) | 2013.07.06 |
| OCP license.E04.130627 (0) | 2013.07.06 |
| OCP license.E03.130626 (0) | 2013.07.06 |
| OCP license.E02.130625 (0) | 2013.07.06 |